This post shows how to use encrypted access tokens with Microsoft Entra ID App registrations using Microsoft.Identity.Web. By using encrypted access tokens, only applications with access to the private key can decrypt the tokens. When using encrypted tokens, you can prevent access tokens data being used or read by such tools as https://jwt.ms or https://jwt.io and prevent the payload claims being read.
Code: https://github.com/damienbod/MicrosoftEntraIDAuthMicrosoftIdentityWeb
Posts in this series
- Implement Microsoft Entra ID Client credentials flow using Client Certificates for service APIs
- Using Key Vault certificates with Microsoft.Identity.Web and ASP.NET Core applications
- Using encrypted access tokens in Azure with Microsoft.Identity.Web and Azure App registrations
- Implement a Web APP and an ASP.NET Core Secure API using Microsoft Entra ID which delegates to a second API
- Using multiple APIs in Angular and ASP.NET Core with Microsoft Entra ID authentication
- Using multiple APIs in Blazor with Microsoft Entra ID authentication
- Microsoft Entra ID Access Token Lifetime Policy Management in ASP.NET Core
- Implement OAUTH Device Code Flow with Microsoft Entra ID and ASP.NET Core
- Implement app roles authorization with Microsoft Entra ID and ASP.NET Core
History
- 2023-11-28 Updated to .NET 8
Setup
Two applications were created to demonstrate the AAD token encryption. An ASP.NET Core application was created which implements an API using Microsoft.Identity.Web to secure the API. The API uses an encrypted token. Secondly, a UI app was created to login to AAD and request the API using the API access_as_user scope. The decryption, encryption certificate was created in Azure Key Vault and the public key .cer file was downloaded. This public key is used in the Azure App Registration for the token encryption.
Setting up the Azure App Registration
The Azure App registration for the Web API is setup to use token encyption. The token which was created in Azure Key Vault can be added to the keyCredentials array in the App Azure Registration manifest file. The customKeyIdentifier is the thumbprint and the usage is set to Encrypt. The value property contains the base64 .cer file which was download from your Key Vault.
"keyCredentials": [
{
"customKeyIdentifier": "E1454F331F3DBF52523AAF0913DB521849E05AD3",
"endDate": "2021-10-20T12:19:52Z",
"keyId": "53095330-1680-4a8d-bf0d-8d0d042fe88b",
"startDate": "2020-10-20T12:09:52Z",
"type": "AsymmetricX509Cert",
"usage": "Encrypt",
"value": "--your base 64 .cer , ie public key --",
"displayName": "CN=myTokenEncyptionCert"
},
]
The tokenEncryptionKeyId property in the Azure App Registration manifest is used to define the certificate which will be used for token encryption. This is set to the keyId of the certificate definition in the keyCredentials array.
"tokenEncryptionKeyId": "53095330-1680-4a8d-bf0d-8d0d042fe88b"
Note: If you upload the certificate to the Azure App registration using the portal, the usage will be set to verify and it cannot be used for token encryption.
Configuration of API application
The ASP.NET Core application uses AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApiAuthentication with the default Microsoft Entra ID configuration. This authorizes the API requests.
public static WebApplication ConfigureServices(this WebApplicationBuilder builder)
{
var services = builder.Services;
var configuration = builder.Configuration;
services.AddSingleton<IAuthorizationHandler, HasServiceApiRoleHandler>();
services.AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApiAuthentication(builder.Configuration);
services.AddControllers();
services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("ValidateAccessTokenPolicy", validateAccessTokenPolicy =>
{
validateAccessTokenPolicy.Requirements.Add(new HasServiceApiRoleRequirement());
// Validate ClientId from token
validateAccessTokenPolicy.RequireClaim("azp", builder.Configuration["AzureAd:ClientId"]!);
// only allow tokens which used "Private key JWT Client authentication"
// // https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/access-tokens
// Indicates how the client was authenticated. For a public client, the value is "0".
// If client ID and client secret are used, the value is "1".
// If a client certificate was used for authentication, the value is "2".
validateAccessTokenPolicy.RequireClaim("azpacr", "2");
});
});
return builder.Build();
}
The app.settings defines the TokenDecryptionCertificates to use the Key Vault Certificate which is used for the token decryption. This is the same certificate which was used in the Azure App Registration. We used the public key from the certificate in the manifest definition.
"AzureAd": {
"Instance": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/",
"Domain": "damienbodhotmail.onmicrosoft.com",
"TenantId": "7ff95b15-dc21-4ba6-bc92-824856578fc1",
"ClientId": "fdc48df2-2b54-411b-a684-7d9868ce1a95",
"TokenDecryptionCertificates": [
{
"SourceType": "KeyVault",
"KeyVaultUrl": "https://damienbod.vault.azure.net",
"KeyVaultCertificateName": "DecryptionCertificateCert2"
}
],
"SendX5C": "true"
},
Configuration of UI application which calls API
The UI application which logins in, gives consent does not require the TokenDecryptionCertificates to use the API. It just uses a ClientCertificates to verify itself. This is not the same certicate and will have a verify usage in the Microsoft Entra ID App Registration manifest.
"CallApi": {
"ScopeForAccessToken": "api://b178f3a5-7588-492a-924f-72d7887b7e48/.default",
"ApiBaseAddress": "https://localhost:44390",
"Instance": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/",
"Domain": "damienbodhotmail.onmicrosoft.com",
"TenantId": "7ff95b15-dc21-4ba6-bc92-824856578fc1",
"ClientId": "b178f3a5-7588-492a-924f-72d7887b7e48",
"ClientCertificates": [
{
"SourceType": "KeyVault",
"KeyVaultUrl": "https://damienbod.vault.azure.net",
"KeyVaultCertificateName": "ServiceApiCert"
}
]
},
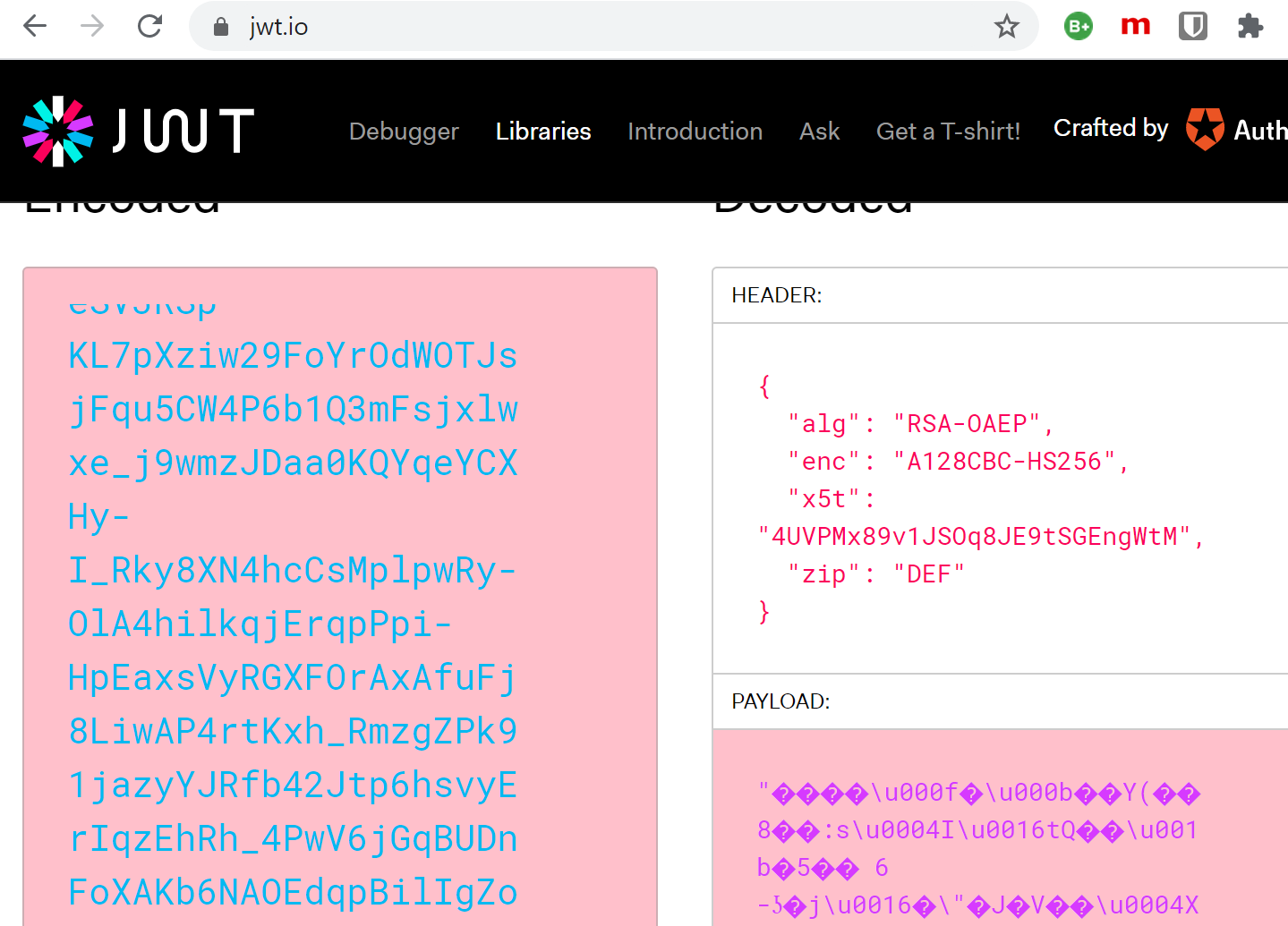
If you start the applications without the App registration token encryption you can debug the application and view the token claims as the default produces a JWT access token.

When using token encryption, the payload can no longer be viewed.
Links
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/manage-apps/howto-saml-token-encryption
Authentication and the Azure SDK
https://github.com/AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-dotnet/wiki/Client-credential-flows
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7523
https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#ClientAuthentication
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/access-tokens
https://github.com/AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-dotnet/wiki/Client-Assertions
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/v2-oauth2-client-creds-grant-flow
API Security with OAuth2 and OpenID Connect in Depth with Kevin Dockx, August 2020
https://www.scottbrady91.com/OAuth/Removing-Shared-Secrets-for-OAuth-Client-Authentication
https://github.com/KevinDockx/ApiSecurityInDepth
https://github.com/AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-dotnet/wiki

[…] Using encrypted access tokens in Azure with Microsoft.Identity.Web and Azure App registrations (Damien Bowden) […]
Hi Damien, i have tried to follow the steps to encrypt the token (like JWE) but it’s not working. Is this feature gone now ?
Hi Argha Sen
I check this, I have read no breaking changes about this. .NET 9 has some changes to the certificate loading. Checking this out.
Greetings Damien
Hi Damien ,
Thank you for quick reply , I was able solve the issue. I need one suggestion, I am thinking to use JWE to protect HTTP trigger based azure function (consumption) api endpoint. Will it slow down the throughput. And I am also thinking to use private_key_jwt client credential flow to connect the azure function from it’s respective client. Should both of these slow down the system.